Results
The two graphs illustrate an exemplary heating process with a setpoint
of 27 degrees Celsius.
The upper graph describes the outdoor and indoor
temperature of the model building and compares them to the setpoint.
Initially, the temperature inside the house was cooled down, resulting
in the outdoor temperature (light blue curve) being higher than the
indoor temperature (orange curve).
It is evident that when increasing
the setpoint, the indoor temperature rises faster than the outdoor
temperature.
Additionally, it can be observed that the slope of the
curve decreases as the setpoint is approached to prevent exceeding the
desired temperature.
The process was interrupted by opening the window,
which lowered the setpoint to 24 degrees Celsius in this example.
Since
the outdoor thermometer is mounted very close to the model building on
the assembly plate due to limited space, the values for indoor and
outdoor temperature are similar.
The outdoor temperature also increases
as the setpoint is raised.
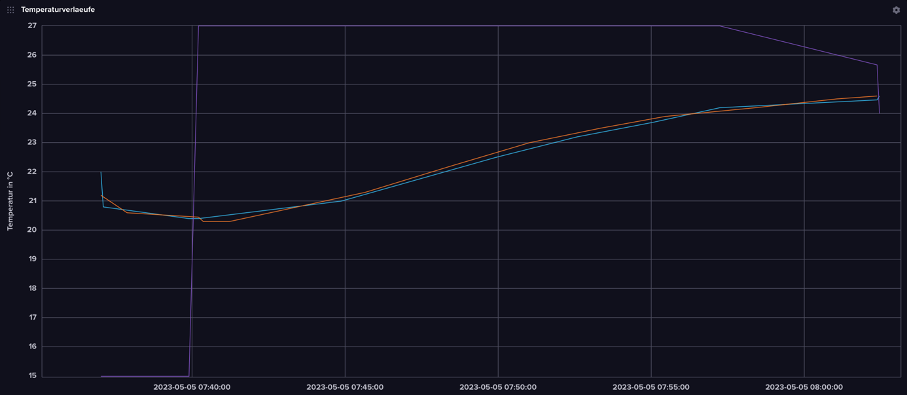 Figure: Temperature curves of indoor and outdoor temperatures, Fabio Bock
Figure: Temperature curves of indoor and outdoor temperatures, Fabio Bock
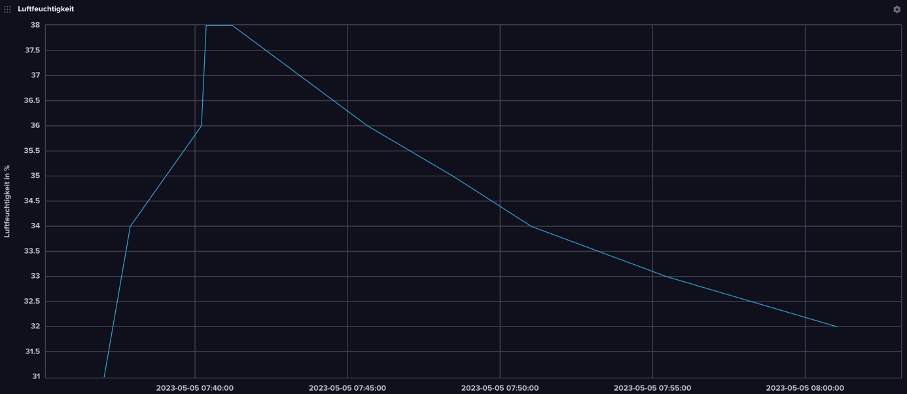 Figure: Humidity curve, Fabio Bock
Figure: Humidity curve, Fabio Bock